GENERAL OVERVIEW
Shift’s Business Model Red Flags is a set of indicators that may be found in dominant or emerging business models in and across a range of sectors. They are not intended to be an exhaustive list but may help spark reflection and enable the identification of additional red flags.
THE BUSINESS MODEL RED FLAGS ARE INTENDED FOR THE USE OF



- Business leaders seeking to identify and address risks to people that may be embedded in the business model, in order to ensure the resilience of value propositions and strategic decisions.
- Lenders and Investors scrutinizing their portfolios for human rights risk, engaging with clients and investees and diagnosing whether significant human rights incidents are likely to be repeated by the company concerned or replicated in other parts of their portfolio. And
- Regulators, analysts and civil society organizations seeking to strengthen their analysis and engagement with companies in order to advance respect for human rights.
There are 24 Business Model Red Flags
(To see an overview chart with all 24 red flags, click here)
The Red Flags are organized around three features of a business model:


HOW EACH RED FLAG IS ORGANIZED
Each red flag is supported by a guidance document, organized into four levels:
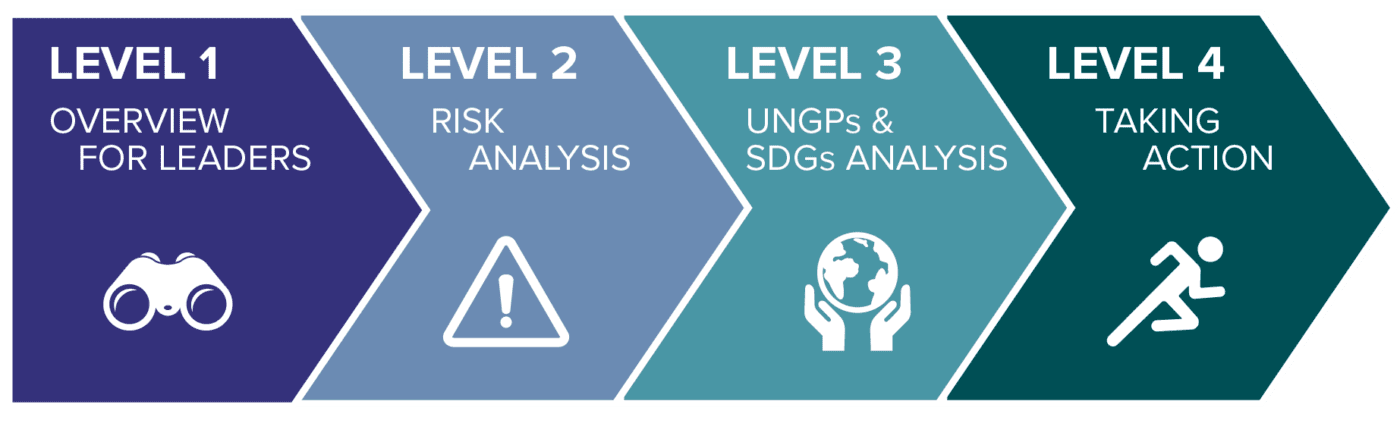
Level One: Overview for Leaders
This includes:
- Higher risk sectors in which the red flag feature is most prevalent;
- Key questions for leaders to ask or be asked to aid decisions about whether further action is needed.
Level Two: Risk Analysis
This includes:
- Risks to People: the key human rights risks associated with this red flag, absent appropriate mitigation efforts;
- Risks to the business: evidence of legal, financial, operational and reputational risks that can arise as a result of companies not addressing the red flag.
Level Three: UNGPs and SDGs analysis
This sets out:
- What the UNGPs say, with particular reference to how companies might be involved with the adverse human rights impacts associated with the red flag;
- Possible contributions to the Sustainable Development Goals that can be achieved with effective mitigation or removal of the red flag;
Level Four: Resources for taking action
This includes:
- Due diligence lines of inquiry for deeper analysis of the company’s impact and how it could effectively mitigate the risks associated with the red flag;
- Mitigation examples illustrating how companies have in practice sought to reduce the impacts associated with the red flag;
- Alternative model examples of companies that have either designed or redesigned their business model to function without the risk elements highlighted in the red flag;
- Additional tools and resources to guide further analysis.

 Business Model Red Flags
Business Model Red Flags  Tool for Indicator Design
Tool for Indicator Design